Dressing for Partial Thickness Burn Using Microbial Cellulose and Transparent Film Dressing : A Comparative Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jpr.v2i2.156Abstract
Background: Wound dressing aims are to create moist and warm condition to accelerate wound healing, decrease level of pain, collects of exudate, decrease the need of dressing changes, cost effectiveness and protection from bacterial contamination. Microbial cellulose creates a moist environment and strong adhesion to the wound to prevent bacterial contamination and protects from temperature changes. Meanwhile transparent film dressing has advantages such as easy to evaluate, rapid rate of epithelialization and provides high comfort for patients. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of microbial cellulose dressing compare to transparent film dressing as control, in the treatment of partial thickness burn.
Method: We perform a single blind randomized clinical trial study. All patients with partial thickness burn with total body surface less than 20% area burns at any age presenting to our burn unit will be included in the study. They were dressed using microbial cellulose and transparent film as control.
Result: The epithelialization rate of patients treated by microbial cellulose was significantly faster and less pain, especially in day 3 and 10 (p=0,000) than those treated with transparent dressing. This study showed patient using microbial cellulose no need to change dressing, meanwhile in transparent dressing it need 2 to 3 times dressing changes and costs more money.
Conclusion: The use of microbial cellulose dressing is a versatile and effective dressing for partial thickness burns. This innovative material will be an alternative dressing in partial-thickness burn wounds.
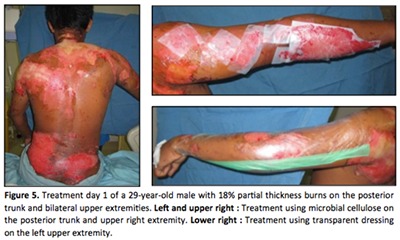
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













