Bacterial Pathogens And Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern In Burn Unit Of Hasan Sadikin Hospital (RSHS) From January 2012 - December 2015
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jpr.v3i2.199Abstract
Background : Infection is the common cause of death following burn injury. Antibiotic resistance is a major wide problem in burn unit. We evaluated the pattern of bacterial pathogens isolated from burn wound and sensitivity of antibiotics in burn unit of RSHS.
Method : A retrospective descriptive study has been done in Burn Unit RSHS by collecting data from burn unit patient’s medical records over 4 years (2012-2015). Data of demography, characteristic of patients, wound isolates bacteria and sensitivity was collected.
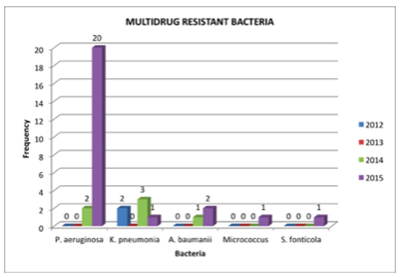
Result : A total of 205 patients were admitted to burn unit of RSHS and 164 patients fulfilled the requirements to be analyzed. 114 (69.5%) patients were male and the most commonly affected age groups were young adults 15-40 years old. The mortality rate in burn unit was 71 patients (43.3%) and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) was commonly the primary cause of death (53.5%) and followed by sepsis (42.3%). Microorganism from burn wound isolates were P. aeruginosa (30.1%), A. baumanii (19.9%), K. pneumonia (19.3%), E. cloacae (9.1%), E. coli (4%), P. stuartii (2.8%). Meropenem was the most sensitive antibiotic against to P. aeruginosa and K. pneumonia. Amikasin was shown to be sensitive to A. baumanii, E. cloacae and E. coli. P. stuartii was 100% sensitive to meropenem, amikasin, piperacillin-tazobactam and cotrimoxazole. Cefoperazon, ceftriaxone and ceftazidime showed very low sensitivity (0-14.3%).
Conclusion : Dominant bacteria isolated was P. aeruginosa which was sensitive to meropenem and commonly resistant to the third generation of cephalosporin antibiotics, which becomes multi drug resistant bacteria.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2016 Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













