Increased Nutrition Intake from Day 1 to Day 7 and Its Correlation with LOS in The Burn Unit of Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jprjournal.v9i2.339Keywords:
Burns, Nutritional Intake, Length of StayAbstract
Introduction : Burn patients as well as the critically ill experience strong oxidative stress, an intense inflammatory response, and a prolonged months-long hypermetabolic and catabolic response that affect nutritional requirements. This study aimed to investigate the nutrition intake in the acute phase from day 1 to day 7 and the correlation with length of stay (LOS) in burn patients in Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital.
Method : This cross-sectional study was conducted from January to December 2020 in the Burn Unit of Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital. Research subjects were burns patients who were willing to take part in this research and met the research criteria. The characteristics data included gender, age, burn area, cause of burns, body mass index, and intake analysis were obtained from medical records and were analyzed using Spearman’s correlation and linear regression.
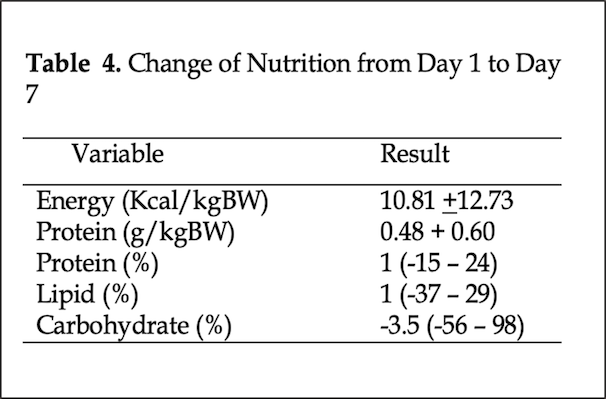
Result : A total of 68 subjects were included in this study. There was an increase in energy intake from day 1 to day 7 of 10.81 + 12.73 Kcal/kgBW. There was a significant negative weak correlation between energy changes from day-1 to day-7 and length of stay (r = -0.25, p = 0.03).
Conclusion: The higher energy increases within 7 days of treatment, the shorter the LOS of burn patients. Further research is still needed to assess the components that influence nutrition intake and how they impact the clinical outcome of burn patients.
References
Moenadjat Y. Luka Bakar: Masalah dan Tatalaksana. 4th ed. Jakarta: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia; 2009
WHO | World Health Statistics 2018: Monitoring health for the SDGs. WHO Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/2018/en/. (Accessed: 24th January 2019)
Wardhana A, Basuki A, Prameswara ADH, Rizkita DN, Andarie AA, Canintika AF. The epidemiology of burns in Indonesia’s national referral burn center from 2013 to 2015. Burns Open. 2017;1(2):67–73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burnso.2017.08.002
Natarajan M, Sekhar R. Nutrition in burns patient. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences. 2015;14(3):38-54.
Singer P, Blaser AR, Berger MM, Alhazzani W, Calder PC, Casaer MP. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin. Nutr. 2019; 38: 48–79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.037
Song C, Chua A. Epidemiology of burn injuries in Singapore from 1997 to 2003. Burns. 2005;31:18–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2004.10.005
American Burn Association NBR. American Burn Association 2012:1–139.
Pujisryani Wardhana A. Epidemiology of burn injuries in Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital from 2009–2010. J Plast Rekonstr. 2010;1:528–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14228/jpr.v1i5.110
Mzezewa S, Jonsson K, Aberg M, Salemark L. A prospective study on the epidemiology of burns in patients admitted to the Harare burn units. Burns. 1999;25:499–504. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-4179(99)00041-8
Ansari-Lari M, Askarian M. Epidemiology of burns presenting to an emergency department in Shiraz, South Iran. Burns. 2003;29:579–81. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-4179(03)00066-4
Chien WC, Pai L, Lin CC, Chen HC. Epidemiology of hospitalized burns patients in Taiwan. Burns 2003;29:582–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-4179(03)00133-5
Ekrami A, Hemadi A, Latifi M. Epidemiology of hospitalized burns patients in Talaghani Hospital during 2003–2007. Bratisl Lek List 2010;111:384–8.
Rousseau AF, Losser MR, Ichai C, Berger MM. ESPEN endorsed recommendations: Nutritional therapy in major burns. Clin Nutr 2013;32:497–502. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2013.02.012
JQ Li, X Han, MJ Zhang, XB Li, GJ Liu, JQ Zhang, et al. Investigation and analysis of protein and energy intake in adult patients with severe burns]. Chinese Journal of Burns 2019; 35(2):143-147.
Oetoro S, Witjaksono FJ, Permadhi I. Tatalaksana nutrisi pada luka bakar. In: Moenadjat Y, ed. Luka Bakar: Masalah dan Tatalaksana, 4th ed. Jakarta: Balai Penerbit FKUI; 2009:285-97.
Prins A. Nutritional management of the burn patient. S Afr J Clin Nutr 2009;22:9-15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/16070658.2009.11734211
Xz Wang CY, Fu PK, Huang CT, Chen CH, Lee BJ, Huang YC. Targeted energy intake is the important determinant of clinical outcomes in medical critically ill patients with high nutrition risk. Nutrients 2018; 10(11): 1731. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111731
Clark, A, Imran J, Madni T, Wolf S. Nutrition and metabolism in burn patients. Burns & Trauma 2017; 5:11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41038-017-0076-x
Demling RH, DeSanti L. Increased protein intake during the recovery phase after severe burns increases body weight gain and muscle function. J Burn Care Rehabil 1998;19(2)161-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00004630-199803000-00015
Jutba A, Kamel A, Cash J, Popp J, Allen A, Roberson L, et al. Impact of an enteral nutrition protocol in critically ill patients with burn injuries. Critical Care Medicine 2022; 50(1): 287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000808688.39677.7f
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Wina Sinaga, Nurul Ratna Mutu Manikam, Aditya Wardhana, Nandita Melati Putri, Lily Indriani Octovia, Akhmad Noviandi Syarif

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













