Facial Hemangioma Treated with Serial Intralesional Corticosteroid Injection: One Year Follow-up
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jpr.v1i3.62Abstract
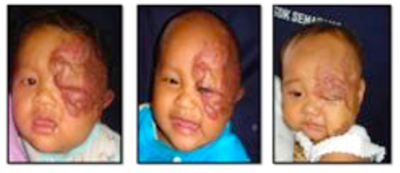
Background: Hemangioma is the most common tumors of childhood, affecting 5 to 10 percent of infants. They have a predilection for the head and neck region. Although having a somewhat predictable natural history evidenced by periods of proliferation, plateau, and involution; the timing of these distinct stages, the presence of complications, and the response to therapy are best characterized as unpredictable. Corticosteroids have been a component of the medical treatment for hemangiomas for over a half century. Intralesional injections purportedly localize the steroid effect to the given lesion and minimize unwanted systemic actions.
Patient and Method : We report six patients with facial hemangioma, who required intralesional corticosteroid injection therapy. The number of corticosteroid injections given varied from 2-5 times at an interval of three weeks. The dosage given was 3-5 mg/kg/injection.
Results : In our six cases, we found a significant decrease in bulkiness. And in three of our cases, patients were able to open their eyes on their own.
Summary :The intralesional corticosteroid therapy was proven to be effective in our case-series.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













