Facial Soft Tissues Reconstruction Methods After Tumor Resection in Soedarso General Hospital 2017 - 2022
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14228/jprjournal.v10i2.355Keywords:
Facial tumor, Malignant tumor, Post tumor resection, Tissue reconstructionAbstract
Introduction: Facial contour deformity is a very challenging problem for aesthetic and reconstructive surgeons. Assessment of facial deformities is important for developing a subsequent reconstruction plan. Various techniques have been described for the repair of tumor-related defects of facial soft tissues. This study aimed to describe methods of Facial Soft Tissue Reconstruction after Tumor Resection at Soedarso General Hospital, West Kalimantan.
Method: A retrospective descriptive study using data such as age, gender, type of tumor, size of the defect, and type of reconstruction done, which were collected from medical records of all patients with malignant facial soft tissue tumors who have underwent tissue reconstruction after tumor resection at Soedarso General Hospital, West Kalimantan, between 2017 and 2022.
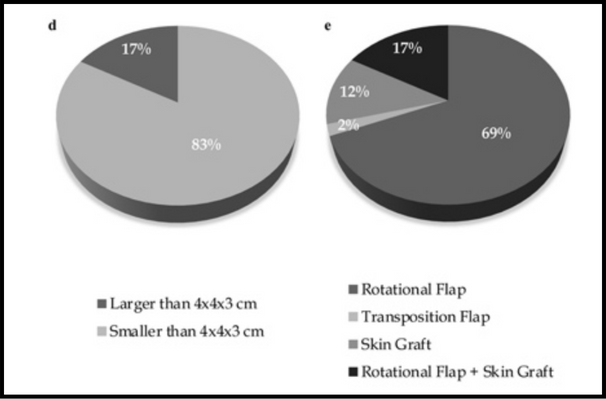
Result: A total of 48 patients were included. 33 patients underwent rotational flap only, 8 patients underwent rotational flap and skin graft, 1 patient underwent transposition flap, 6 patients underwent skin graft. 39 patients had BCC, 7 patients had SCC, 1 patient had MM, 1 patient had Meibom gland Adenocarcinoma. 25 patients were female, 23 patients were male. 41 patients had age 60 years old and older, 7 patients had age younger than 60 years old. 8 patients with defect size larger than 4x4x3 cm, 40 patients with defect size smaller than 4x4x3 cm.
Conclusion: Knowledge of distribution patterns of facial soft tissue tumors will help to correctly choose the right options in facial reconstruction. Unawareness can lead to inadequate treatment with serious consequences for the affected patient.
References
Issa SA, Jameel ME. Free Dermal Fat Graft for Reconstruction of Soft Tissue Defects in the Maxillofacial Region. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2020;13(4):260-266. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1943387520910678
Dey JK, Ishii M, Boahene KD, Byrne P, Ishii LE. Impact of facial defect reconstruction on attractiveness and negative facial perception. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(6):1316-21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25130
Muzic JG, Schmitt AR, Wright AC, Alniemi DT, Zubair AS, Olazagasti Lourido JM, Sosa Seda IM, Weaver AL, Baum CL. Incidence and Trends of Basal Cell Carcinoma and Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Study in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 2000 to 2010. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92(6):890-898. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2017.02.015
Davis DS, Robinson C, Callender VD. Skin cancer in women of color: Epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7(2):127-134. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.01.017
Huang CH, Qian HG, Zhao XY, Shen GL, Lin W, Qi Q. Repairing Facial Soft Tissue Defects by Swelling Anesthesia after Tumor Resection with Narrow Pedicle Flaps. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(15):6761-3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.15.6761
Oh CC, Jin A, Koh WP. Trends of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma among the Chinese, Malays, and Indians in Singapore from 1968-2016. JAAD Int. 2021;4:39-45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdin.2021.05.006
Lee KS, Kim JO, Kim NG, Lee YJ, Park YJ, Kim JS. A Comparison of the Local Flap and Skin Graft by Location of Face in Reconstruction after Resection of Facial Skin Cancer. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2017;18(4):255-260. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7181/acfs.2017.18.4.255
Frank SA. Dynamics of Cancer: Incidence, Inheritance, and Evolution. Princeton (NJ): Princeton University Press; 2007. Chapter 2, Age of Cancer Incidence. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1559/
Gordon R. Skin cancer: an overview of epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2013;29(3):160-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soncn.2013.06.002
Moy J, Wax MK, Loyo M. Soft Tissue Reconstruction of Parotidectomy Defect. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2021;54(3):567-581. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2021.02.009
Erkul E, Patel KG, Day T. Surgical Planning for Resection and Reconstruction of Facial Cutaneous Malignancies. Int J Head Neck Surg. 2016;7(3):149-164. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1281
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Fidi Bhawana Jaya, Doni Setiawan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of the article and grant Jurnal Plastik Rekonstruksi the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Articles opting for open access will be immediately available and permanently free for everyone to read, download and share from the time of publication. All open access articles are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-NoDerivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) which allows readers to disseminate and reuse the article, as well as share and reuse of the scientific material. It does not permit commercial exploitation or the creation of derivative works without specific permission.













